As the hearing health landscape evolves, it’s essential to understand the differences between traditional hearing aids , the newer over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids and Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAP’s). This knowledge helps individuals make informed decisions about their hearing care and choose the best solution for their needs.
This blog post is derived from a chapter in my book “Unlocking The World of Over-The-Counter Hearing Aids: A Consumer’s Guide”, with the addition of an discussion on Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs). If you would like to read my book, it’s available here.
Personal Sound Amplification Products
Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs) are distinct from hearing aids and are not intended to treat hearing loss, although they are often used for this purpose. It is not recommended to use them as ‘hearing aids’. Instead, PSAPs are designed to help individuals with normal hearing amplify sounds during activities such as hunting. Classified as electronic devices, they are not subject to the same regulations as hearing aids or OTC hearing aids. As a result, they lack the advanced processing capabilities needed to accommodate various configurations of hearing loss. Typically, PSAPs can be found in stores priced between $200 and $400.
Traditional Hearing Aids
Traditional hearing aids are custom fitted devices prescribed by Audiologists or Hearing Instrument Specialists. They are designed to cater to a wide range of hearing loss severities, from mild to profound. Hearing aids are very sophisticated devices with robust sound processing capabilities. They offer a wide range of options the Audiologist or Hearing Instrument Specialist can adjust within the programming software to ensure the devices are set up appropriately for your hearing loss and sound quality preferences.
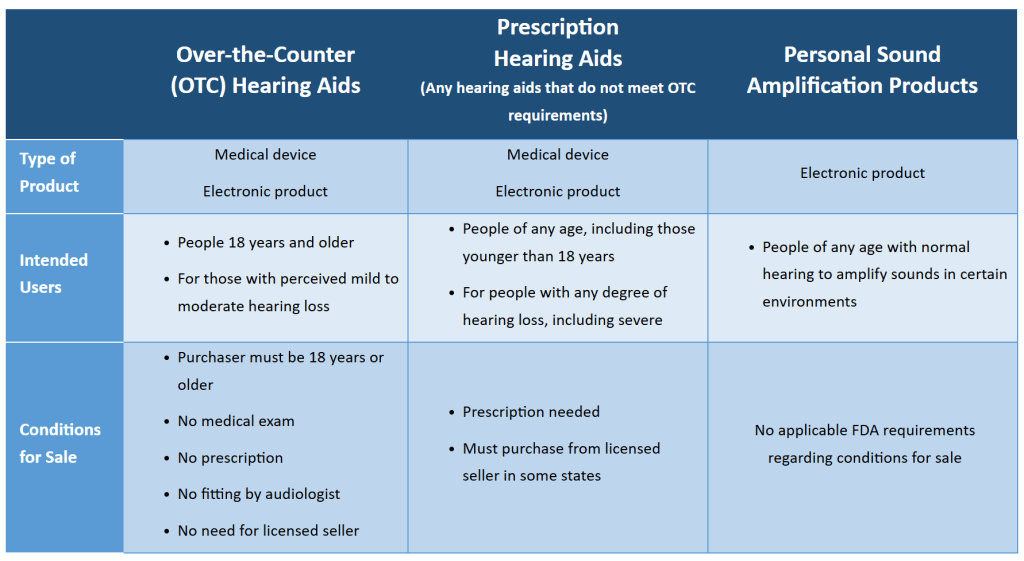
Screen capture from https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/hearing-aids-and-personal-sound-amplification-products-what-know
Key Features:
Customization and Fitting:
- Custom-fitted to the individual’s ear anatomy.
- Fine-tuned to match the specific hearing loss profile of the user.
- Requires professional fitting and adjustment.
Technology and Features:
- Advanced sound processing technologies.
- Features like directional microphones, feedback reduction, and noise cancellation.
- Connectivity options to smartphones and other devices.
Professional Support:
- Includes comprehensive hearing evaluations.
- Ongoing support and adjustments from Audiologists.
- Regular check-ups to ensure optimal performance.
Cost:
- $3000-$8000 per pair
- Generally, they more expensive due to professional services and the availability of more advanced technology.
- Occasionally covered partially or fully by insurance, depending on the provider and plan. Third party hearing aid discount plans are on the rise.
Pros:
- Personalized and precisely tuned to the user’s hearing needs. Can accommodate more complex and severe to profound levels of hearing impairment.
- Professional support ensures proper fitting and ongoing care.
- Advanced features provide high sound quality and better performance in challenging listening environments.
- Include repair services and loss & damage coverage.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to OTC hearing aids.
- May require multiple visits to a hearing care professional for fitting and adjustments.
OTC Hearing Aids
OTC hearing aids are designed to be purchased directly by consumers without the need for a prescription or professional fitting. They are suitable for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss and offer a more accessible and affordable option. They have minimal capabilities for customization and sound quality adjustments.
Key Features:
Accessibility:
- Available for purchase online, in pharmacies, or retail stores.
- No need for a hearing test or prescription from a professional.
User-Friendly Design:
- Designed for self-fitting with user-friendly instructions.
- Often include smartphone apps for customization and adjustments.
Cost:
- Generally, they are more affordable than traditional hearing aids costing about $1500 per pair.
- No additional costs for professional fitting and follow-up appointments.
Pros:
- More accessible and affordable, making them an attractive option for many.
- Easy to purchase and use, with less stigma attached to buying them compared to traditional hearing aids.
- Approved for those with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss who are comfortable with self-fitting and adjustments.
Cons:
- Not as customizable as traditional hearing aids.
- Limited professional support and follow-up care.
- Are not suitable for individuals with severe or profound hearing loss.
- Does not include any repair or loss & damage coverage.
Choosing the Right Option
Who Should Consider Traditional Hearing Aids?
- Individuals with moderate to profound hearing loss.
- Those who prefer personalized fitting and ongoing professional support.
- Users looking for advanced features and superior sound quality.
- Individuals with complex hearing needs or specific lifestyle requirements.
Who Should Consider OTC Hearing Aids?
- Individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
- Those seeking a more affordable and accessible solution.
- Users comfortable with self-fitting and managing their hearing aids.
- People looking for a quick and convenient way to improve their hearing without visiting an Audiologist.
Understanding the differences between traditional and OTC hearing aids is crucial for making an informed decision about your hearing care. While traditional hearing aids offer personalized fitting and advanced features, OTC hearing aids provide a more accessible and affordable option for those with mild to moderate hearing loss. By considering your specific hearing needs, lifestyle, and budget, you can choose the hearing aid that best suits your situation and take a significant step towards better hearing health.
Refences:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Personal_sound_amplification_product
